No products in the cart.
A detailed guide for foreign investors on Laos’ legal requirements, including licensing, approvals, ownership rules, profit repatriation, and compliance obligations.
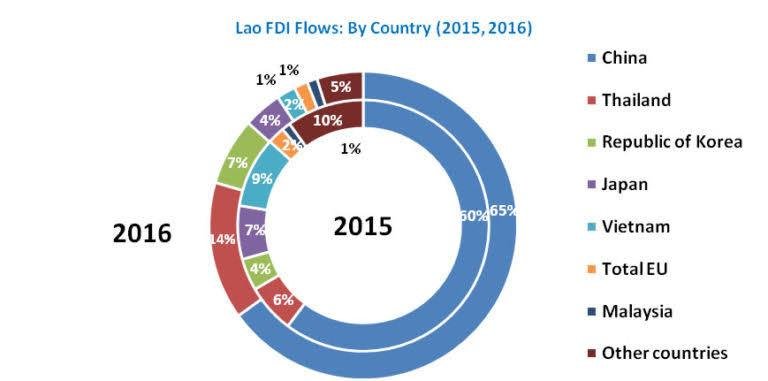
Laos has positioned itself as an attractive destination for foreign investment due to its strategic location in Southeast Asia, political stability, and membership in ASEAN. However, foreign investors must comply with specific legal requirements before establishing operations. This article provides an overview of the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) framework in Laos and the compliance obligations investors must fulfill.
Legal Framework for FDI in Laos
FDI in Laos is primarily regulated under the Investment Promotion Law and related decrees. The Ministry of Planning and Investment (MPI) oversees the approval and monitoring of foreign investment projects. Certain industries may be restricted or subject to special conditions, particularly those related to natural resources or national security.
Investment Approval Process
The investment approval process generally involves:
1. Submitting a detailed investment proposal to the MPI.
2. Reviewing sector-specific approvals from relevant ministries.
3. Registering the enterprise with the Ministry of Industry and Commerce.
4. Obtaining a business license and tax registration.
The process may vary depending on the type of investment and sector.
Ownership Rules and Equity Requirements
Laos permits 100% foreign ownership in many sectors, though certain industries may require joint ventures with Lao partners. Equity requirements differ depending on whether the project is in a general business, concession-based activity, or a priority sector under the Investment Promotion Law.
Taxation and Profit Repatriation
Foreign investors are subject to Lao corporate income tax and other applicable taxes. However, tax incentives may be available for investments in priority sectors or special economic zones (SEZs). Laos allows foreign investors to repatriate profits after meeting tax obligations, subject to foreign exchange regulations.
Compliance and Reporting Obligations
Investors must maintain proper accounting records, submit annual financial statements, and comply with labor and environmental laws. Failure to comply may result in penalties, suspension of licenses, or revocation of investment approvals.
Risks and Challenges for Foreign Investors
Challenges include lengthy approval processes, bureaucratic delays, unclear land use rights, and limited infrastructure in some areas. Foreign investors may also face difficulties in navigating local language and cultural differences.
Best Practices for FDI Compliance
To ensure successful investment in Laos, foreign investors should:
- Conduct thorough due diligence on legal and regulatory requirements.
- Work with local legal and business advisors.
- Ensure contracts and agreements are properly registered.
- Maintain open communication with government authorities.
- Leverage investment incentives in SEZs and priority sectors.
These practices help minimize risks and ensure regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
Laos offers attractive opportunities for foreign investors, but compliance with legal and regulatory requirements is essential. By understanding the FDI framework, securing proper approvals, and adhering to compliance obligations, investors can establish a strong presence in the Lao market.
About CITS Laos
CITS Laos supports foreign investors by providing end-to-end advisory services on FDI compliance, licensing, and approvals. We help investors navigate legal complexities, obtain necessary permits, and optimize investment strategies to succeed in Laos’ growing economy.